As the world becomes more conscious of the environmental impact of human activities, there has been a growing interest in sustainable architecture. One aspect of sustainable architecture that has gained significant attention in recent times is green roofs. Green roofs, also known as living roofs or vegetated roofs, are roofs that are partially or completely covered with vegetation. In this article, we will take you on a journey through the history of green roofs, their evolution, types, benefits, examples, challenges, regulations, and maintenance.

Introduction to Sustainable Architecture and Green Roofs
Sustainable architecture is an approach to building design that prioritizes the use of environmentally friendly materials, energy efficiency, and the reduction of carbon emissions. The goal of sustainable architecture is to create buildings that have minimal impact on the environment and are healthy and comfortable for occupants. Green roofs are an excellent example of sustainable architecture because they provide multiple benefits to the environment and building occupants.
Green roofs have been in use for thousands of years, but it is only in recent times that they have become popular in modern architecture. The concept of green roofs can be traced back to ancient civilizations in Europe and the Middle East, where people would cover their homes with earth and vegetation to keep them cool in the summer and warm in the winter.
The History of Green Roofs and Their Evolution
The modern green roof movement began in Germany in the 1960s, when innovative architects started experimenting with the concept of green roofs. The first modern green roof was built in Germany in 1960 by architect Friedensreich Hundertwasser. The roof was covered with soil and plants and had a pond with fish and turtles. Hundertwasser believed that green roofs were essential for the future of urban planning because they provided a way to bring nature back into the city.
Since then, green roofs have evolved significantly, and today there are three main types of green roofs: extensive, intensive, and modular. Extensive green roofs are lightweight and have shallow soil depths, making them suitable for buildings with a low load-bearing capacity. Intensive green roofs have a deeper soil depth and can support a wider variety of plants, including trees. Modular green roofs are pre-planted modules that can be easily installed and replaced.
Types of Green Roofs
Extensive Green Roofs
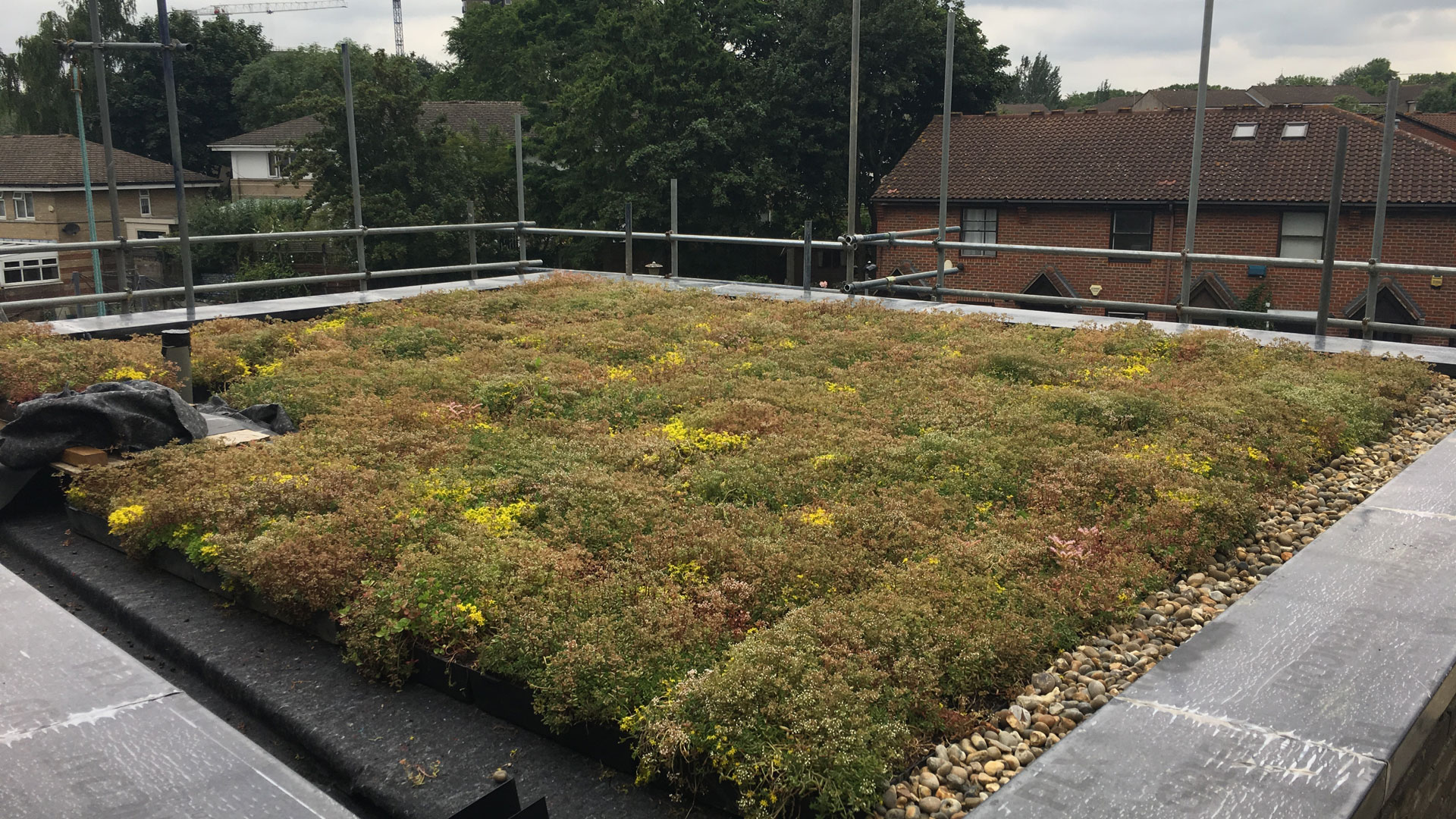
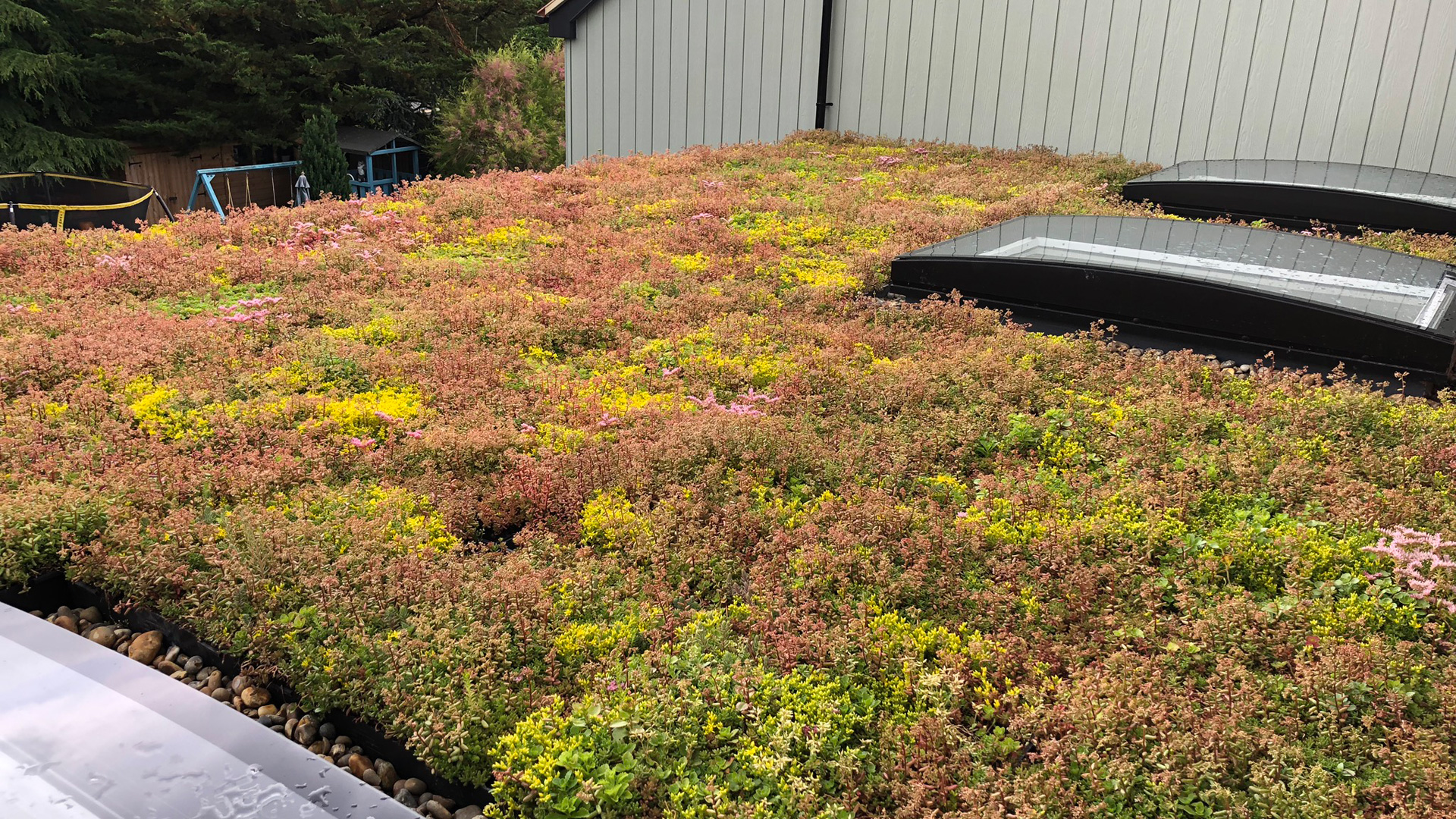
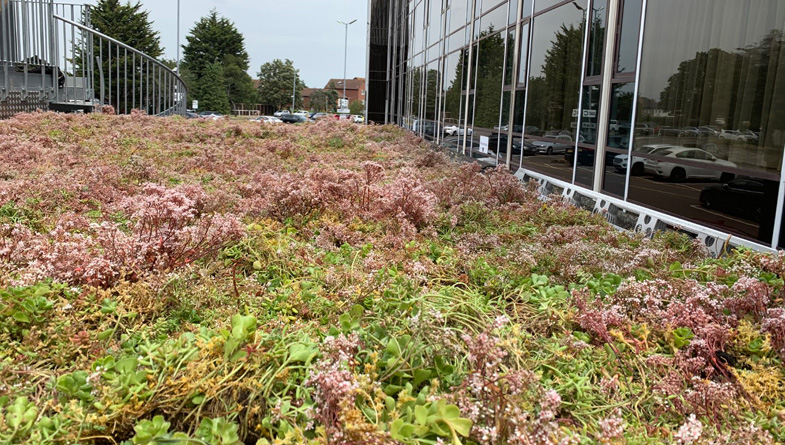
Extensive green roofs are designed to be lightweight and require minimal maintenance. They are typically covered with sedum, grasses, and other low-growing plants that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Extensive green roofs are ideal for buildings with a low load-bearing capacity, such as residential homes and small commercial buildings.
Intensive Green Roofs
Intensive green roofs are more like traditional gardens and require regular maintenance. They are designed to support a wider variety of plants, including trees, shrubs, and flowers. Intensive green roofs have a deeper soil depth, allowing for more complex planting arrangements. They are typically installed on larger commercial buildings and public spaces.
Modular Green Roofs
Modular green roofs consist of pre-planted modules that can be easily installed and replaced. They are designed to be lightweight and require minimal maintenance. Modular green roofs are suitable for buildings with a low load-bearing capacity and can be used on both residential and commercial buildings.
Benefits of Green Roofs
Green roofs provide numerous benefits to the environment, building occupants, and the community. Here are some of the benefits of green roofs:
Environmental Benefits
- Green roofs reduce the urban heat island effect by absorbing heat and reducing the temperature of the surrounding air.
- Green roofs help to reduce stormwater runoff by absorbing rainwater and releasing it slowly over time.
- Green roofs improve the air quality by absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen.
- Green roofs provide habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife, increasing biodiversity in urban areas.
Economic Benefits
- Green roofs can help to reduce energy costs by providing insulation and reducing the need for air conditioning in summer and heating in winter.
- Green roofs can increase the lifespan of roofs by protecting them from weathering and erosion.
- Green roofs can increase the value of a property by improving its aesthetic appeal and providing additional living space.
Social Benefits
- Green roofs provide a space for building occupants to relax and enjoy nature.
- Green roofs can help to improve the mental health and well-being of building occupants by providing a connection to nature.
- Green roofs can help to reduce noise pollution by absorbing sound waves.
How Green Roofs Help Combat Climate Change
Green roofs play an essential role in combatting climate change by reducing carbon emissions and increasing carbon sequestration. Green roofs reduce carbon emissions by reducing the need for air conditioning in summer and heating in winter, thus reducing the energy consumption of buildings. Green roofs also absorb carbon dioxide from the air and store it in the soil and vegetation. This process is known as carbon sequestration and helps to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Examples of Green Roofs Around the World
Green roofs are becoming increasingly popular around the world, and there are many excellent examples of green roofs in different countries. Here are some examples of green roofs around the world:
1. The High Line, New York City
The High Line is a public park built on an elevated railway line in New York City. The park features extensive green roofs that provide habitats for birds and insects and help to reduce the urban heat island effect.
2. The Bosco Verticale, Milan
The Bosco Verticale, or Vertical Forest, is a residential building in Milan that features over 900 trees and 20,000 plants on its balconies and terraces. The building provides habitats for birds and insects and helps to improve the air quality in the surrounding area.
3. The School of Art, Design, and Media, Singapore
The School of Art, Design, and Media at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore features a green roof that provides insulation, reduces stormwater runoff, and provides habitats for birds and insects.
Challenges of Green Roof Implementation
Despite the many benefits of green roofs, there are also several challenges associated with their implementation. Some of the main challenges include:
1. Cost
Green roofs can be expensive to install and maintain, making them less accessible to lower-income households and businesses.
2. Structural Limitations
Green roofs require a strong structural foundation to support the weight of the soil, plants, and water. Buildings with a low load-bearing capacity may not be suitable for green roofs.
Green Roof Regulations and Policies
Governments around the world are recognizing the importance of green roofs and are implementing policies and regulations to encourage their adoption. In the United States, several cities, including New York City, Chicago, and San Francisco, have green roof programs that provide incentives for building owners to install green roofs. In Canada, Toronto has a bylaw that requires new developments to have a green roof or a solar panel system.
Green Roof Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintaining a green roof requires regular attention to ensure that the plants remain healthy and the roof functions as intended. Some of the maintenance tasks include watering, weeding, fertilizing, and pruning. It is essential to hire a professional to maintain a green roof because they have the expertise and equipment necessary to do the job correctly.
Conclusion – The Future of Green Roofs in Sustainable Architecture
Green roofs are an excellent example of sustainable architecture and provide numerous benefits to the environment, building occupants, and the community. Despite the challenges associated with their implementation, green roofs are becoming increasingly popular around the world, and governments are implementing policies and regulations to encourage their adoption. As we continue to prioritize sustainability in building design, green roofs will undoubtedly play an essential role in creating a more sustainable future.
If you are interested in installing a green roof on your property, contact us to discuss your options and learn more about the benefits of green roofs. To find out more about the M-Tray® instant modular green roof solution from Wallbarn, please click here.